13.003 Computational Geometry and Visualization
Rotation
glRotate{fd}(a, x, y, z);
where a is the (right-handed) rotation angle, given in degrees, and (x, y, z) define the axis of rotation.
C' = CR
where
R = 0
M 0
0
0 0 0 1
where M is a general 3x3 rotation matrix.
Note the following three special cases of rotation about the coordinate axes.
glRotatef(a, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
R = 1 0 0 0
0 cos(a) -sin(a) 0
0 sin(a) cos(a) 0
0 0 0 1
glRotatef(a, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
R = cos(a) 0 sin(a) 0
0 1 0 0
-sin(a) 0 cos(a) 0
0 0 0 1
glRotatef(a, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
R = cos(a) -sin(a) 0 0
sin(a) cos(a) 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1
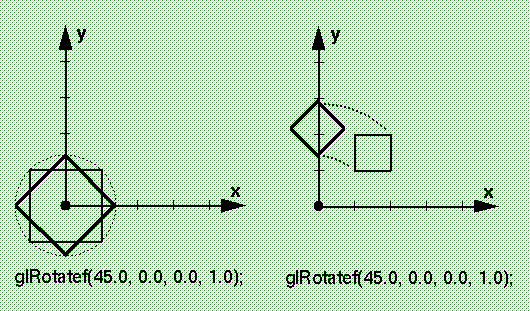
Like scaling, rotation is performed relative to the origin of the current coordinate system.
